Employee retention speaks volumes about an organizations culture, work environment and sometimes even management. What can organizations do to improve employee retention rates? It starts with employee recognition and ensuring the right channels are in place for encouraging kudos to achieve high employee retention rates.
If Content is King, then How Do You Help it Rule Your Intranet?
Where does Intranet fit in Your Digital Workplace Strategy
Summary:
Your Digital Workplace is not a single tool. It’s a set of tools that make work possible by complimenting each other. By evaluating new tools that come on the market in terms of their fitness on your roadmap, you can avoid tools that are roadmap-distractions and require costly backtracking. Intranets have some very clear goals and purpose in comparison to other communication tools, but you have to ensure governance and adequate support in order to make the investment worthwhile.
1. Digital Workplace: Understanding
A bit more than a year ago, at Microsoft Ignite Conference in Orlando, I had a chance to speak with Joe Francis who runs a Yammer network for over 200,000 users at Glaxo Smith Kline.
Joe and their MS Partner Leslie provided some real close-up looks on how they manage their Yammer network and how it has transformed communication within their organization.
At the time, Yammer was known in the Microsoft community to be on the “decline“. I spoke with several SME’s in the area and everyone had a nervous feeling what’s going to happen with the product. And yet it does so well at GSK.
Just 5 years ago, Yammer was considered a disruptor and many claimed it will displace SharePoint as a communication tool. But it didn’t. Now, similar disruptor stories are told about Microsoft Teams.
Many organizations are struggling to figure out how Microsoft Teams and other tools in Office 365 suite will fit their digital landscapes.
How do you know when a new tool is right for the organization?
First, let’s understand what a Digital Workplace is:
A Digital Workplace is a cohesive set of tools and environments which help the company operate successfully and drive towards a business goal.
Few key characteristics:
Each tool must have its purpose and audience in your organization
For example: you’re not trying to do project management with Yammer, just as you wouldn’t use Microsoft Project for employee communication
There is a governance around each tool and business users are not confused
Users are not mistakenly putting confidential files onto an externally accessible network
The tool belongs to a roadmap
It’s not a rogue tool installed out of someone’s impatience. Even if it’s an ad-hoc solution, it needs to have a roadmap and transition plan
2. Is the Tool a Distraction or does it belong to a roadmap?
Now that we know what the Digital Workplace is and that it can have several tools in its arsenal, let’s define the “distraction” on a roadmap.
The Roadmap
Your roadmap is a way to go from point A (now) to point B (say, 3 years from now).
A tool that is a distraction will take you on a side road and lead nowhere so you’ll have to backtrack to get back on the right path.
There are a few characteristics of a digital tool that make it a distraction.
Tool is a distraction if
It’s a short term “band-aid”; not tied to solving a business goal for the company
Example: A team needs to collaborate with a contractor who doesn’t have a corporate account, so they create a Dropbox account for them to share files with.
This action does not create a strategy for sharing files externally, it’s simply a band-aid for this one case
It doesn’t fit core values or policies of the business
Example: Help-desk team using email to ask customer for passwords
This action can result in breaches and customer information leaks
It doesn’t scale with growing demand
Example: Using Microsoft Teams channels to store project documentation
This decision might make sense temporarily but as more projects you’re assigned to, the more channels you’ll have and searching, archiving, and accessing relevant deliverables will become a nightmare as the team grows
It has visible negative impact on business goals
Example: Email blast company news
This clogs people’s email. They stop paying attention to newsletters and miss important announcements resulting in disengagement
3. Where does the intranet fit into all this?
Intranet revolves around these key goals:
Be a hub for reliable corporate communication (leadership communication, KPIs etc)
Be a one-stop-shop for corporate knowledge (templates, samples, Knowledgebase, How to’s)
Be a central spot for resources that employees need to get their job done (manuals, policies, request forms)
Be a one-stop-shop for collaboration (including: document management, findings skills and expertise through directories, launching key forms such as HR forms)
Additionally, if you don’t have any overlapping tools such as HRMS systems, your intranet can also be a place for:
Employees to connect (employee news, events, and ideas contributions)
Staff Engagement (shout-outs and kudos)
4. Setting up your intranet for success
As Joe mentions in his interview about Yammer, you have to plan for success.
Here are the key steps to implement your intranet successfully:
Solutions
Obtain Executive buy-in
Propose a pilot project. Set targets, measure outcomes, report results
Avoid the trap of Planned Obsolescence
Planned Obsolescence has several shades, here are few examples
Example 1: Instead of maintaining the service subscription companies do not renew it hoping the software will just work. Instead, the software becomes stale and users become dissatisfied with its performance
Example 2: No budget assigned for an internal resource to collect employee requests, prioritize, and action them
Example 3: No budget for increased demand on helpdesk resources when rolling out a new software
Equally represented content
Content on the intranet is often heavily tilted towards communications with very little representation for the areas of the business. This reduces your audience and engagement.
Build intuitive information architecture
Not being able to find things on the intranet is one of the most common frustrations that users report
Test efficiency of your information architecture
Lock down major areas
Target your communication
Split news into global and targeted. Separate people news/watercooler from company news. Separate company-wide alerts (ex.: outage alerts) from news
Launch and Post launch activities
We’re here to help
Struggling to understand how Office 365 toolset fits the digital landscape in your organization?
It’s not always simple, and requires expertise to help you gain insight in the roadmap Microsoft has for its products. We’re here to help you.
We’d be happy to help you with a transparent and objective consultation to get you on the right track and maximize your existing Office 365 investment.
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
4 Best Practices for Evolving Internal Communications to Digital
Social Intranet Features: What They are and How To Use Them
7 Reasons Why Your Intranet is Becoming Stale and Deserted
Building a Business Case for a new Office 365 Intranet
Summary: Building an intranet business case solely focused on numbers is logical but rarely convinces decision-makers to take the next steps. Tie your intranet business case to customer experiences, and show how having a robust intranet helps your organization serve customers better. Start small, embrace iterative stages, and evolve with the Office 365 toolkit.
Why do you need an intranet
Before jumping into how will the intranet be built and what features will it have, we need to start with basics and supply relevant evidence on why do we think we need an intranet.
Go beyond Comparison
When building an intranet business case, it’s natural to try and appeal to decision-makes only in a very quantifiable way. However, this approach only covers surface issues and misses the opportunity to address more complex scenarios.
Say an organization uses file share to collaborate and manage files and other information. Your decision makers are very familiar with the existing file share, what it does, and costs associated with it.
Let’s say existing problems with file share have been identified as:
Cost of growing and maintaining storage
Lack of proper versioning
Cumbersome remote access
To address these, you might focus on:
Up to 1 TB of storage for $X/user/month
Version control included
Remote access included
Are these the only challenges your organization can solve with Office 365?
Here are few more to consider:
Eliminating rework by providing samples and templates
Reducing reliance on email by improving search
Reducing errors by introducing How To’s and Procedure Directory
Simplifying onboarding with the Welcome library
Eliminate bottlenecks for finding information
Align inconsistent processes
Promote knowledge sharing and engagement
Next, let’s see how we can provide compelling evidence to support above claims.
Provide relevant evidence
Regardless of how many benefits implementing a brand-new intranet will bring, you need to supply relevant evidence for your organization.
Here is an example of 2 statements. Which one sounds more compelling?
According to LinkedIn study the Cost of Reworking Information on average is estimated 30% of employee effort over a year. In our organization of 300 desktop users, this means 3,600 of hour/week is lost due to people recreating information that could not be found.
In a past year we have increased staff count by 50 new employees. With new employees onboarding, quick access to existing samples, processes, how to’s, and templates is needed to reduce the cost of recreating information. According to LinkedIn study, the Cost of Reworking Information on average is estimated 30% of employee effort over a year. In our organization of 300 desktop users, this means 3,600 of hour/week is lost due to people recreating information that could not be found.
Both statements offer industry research. The difference between the two is that second statement provides relevant evidence for the organization and not a generic assumption. In fact, I’d argue that ratio of rework hours is even higher because with 50 brand new employees, the learning curve is much steeper.
Tie your intranet to improving customer experiences
Employee efficiencies are tied to customer experiences whether direct or indirect.
When building an intranet business case, ensure this link is clearly visible.
For example, see the difference:
By building a reliable intranet information architecture and testing it prior to launch with the staff, we will improve information findability and reduce errors.
Our staff relies on search efficient results to find relevant client documents and deliverables. By building a reliable intranet information architecture and testing it prior to launch with the staff, we will improve information findability and reduce errors and client escalations.
The simple link to client results instantly elevated the value of proper information architecture design and testing, as opposed to ad-hoc site structure rollout.
How will you deliver a company intranet
Now that you have clear evidence why you need an intranet in your organization, we need a plan on how to get there.
Here are key aspects to consider for your intranet business case when describing the “how”.
Focus on iterative nature of the intranet
Long gone are the days when an intranet required a team of 20 stakeholders and 3 years to launch. The timelines have shortened and companies deliver relevant and useful intranet in an iterative fashion.
The benefits of the iterative approach are:
Reduced risk of timeline and budget slip
Smaller core teams
Focus on function, and value; less on widgets and changing features
Organic adoption
Iterative doesn’t mean barely functioning or bare-bones product. Your intranet roadmap needs to be driven by business priorities.
In your business case, provide the approach of how you plan to determine core scope. In this post on 4 Easy Steps to Effectively Prioritize Your Intranet Scope you will see the diagram on how we get from ideas to action when it comes to scope planning.
It comes down to laying out all of the priorities, and plotting them on the priority and feasibility spectrum.
Embrace diverse toolkit
Any given organization uses a wide set of tools for business. An intranet is not there to replace all of them. It’s important to help guide a clear scope for your intranet, and what the intranet is not.
The decision makers will appreciate a business case which is clear in its goals and embraces diversity of the tools that various teams are using.
What will you need to support your initiative
The final step in your intranet business case should be the support you require to continue.
Resources
To support the design and rollout activities, you will need adequate attention from stakeholders during the design phase as well s continuous support once the intranet is launched.
Here is the guidance in terms of support you need depending on the size of your company:
| Organization Staff Size | Intranet Project Team Size | Operational Team Size (FTE) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 6 | 0.5 |
| 1000 | 7 | 1 |
| 10,000 | 9 | 2 |
Technology/Vendor
Over the years, according to Nielsen Norman report on award winning intranets, intranet teams have engaged external resources to help in their redesign projects, both to fill internal team gaps and gain outside experience and perspective.
In recent years, especially for Office 365 intranets, companies realized that using intranet-in-a-box products such as Origami to gain deployment efficiencies, reduce implementation costs, and dramatically increase usability of their intranets.
Budget
To assess your budget, ensure you count the time required from internal resources, vendors, and cost of the product. Remember to account for the operational team once the intranet has launched. Depending on the size of the organization, the team can range from a part-time to a couple of full-time resources as you can see in the table above.
We’re here to help
Building a compelling business case for an intranet sometimes needs a little bit of collaboration. If you’d like to work together to help you build an engaging business case for your organization, we’re here to help. We have a wealth of techniques to help you drive the right support among your stakeholders.
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
Branding an Intranet: Guidelines for Logo, Name, and Style
Intranet branding is often confused with the user interface design. Although user interface is part of the brand there are more elements to it such as: intranet logo, intranet name, tone of writing, and design.
In this post we’ll take a look at some of the best practices when it comes to branding your intranet to make it relatable to your organization.
Style Guide & Theme
When building a brand new or redesigned intranet, many organizations reuse their public-facing website style guide.
Style guides typically contain:
Logo usage guidelines
Colors
Fonts and typography
Image usage best practices etc
There is nothing wrong with using your public-facing style guide for an intranet, but it’s important not to copy the public website’s look and feel completely.
Here is why:
Avoid Source Confusion
Often times intranet contains links to your public site. We’ve seen users confused when they click on the link in the intranet and end up on the public site thinking they’re still on the intranet. This is more typical for intranets which have near-identical design as the public site. Try to avoid that.
Remember Intranet Use Cases
Another element to consider are the types of devices people will be using when working with the intranet. This will dictate:
Supported screen resolutions. Intranets typically support wider screens to utilize screen real estate for document management
How you present content on the site. Intranet users come to your intranet much more often and content needs to be optimized for quick access.
How do you handle mobile devices. Mobile is less prominent for the intranet and you may save budget with only branding key areas where mobile access is important, as opposed to entire site.
Remember Intranet Audience
How and what you target as your intranet audience will drive what content should be on it.
Content targeted to employees and staff is different from content you write on the web. The table below illustrates how the audience and technology is quite different between platforms.
Public sites usually have a dedicated team authoring and maintaining the content. Intranet in turn is usually a part-time team of contributors.
|
|
Audience |
Technology |
Capabilities |
|
Public-facing website |
Millennials |
Opensource that’s highly flexible |
Full-time large team, fair budget, fair timeline |
|
Intranet |
Millennials, Gen-X, Baby Boomers |
Intranet solution (ex.: Office 365) that does the heavy lifting, but dictates much of the UI design |
Part-time small team, small budget, short timeline |
Source: Nielsen Norman Group
Style Guide Best Practices
With that, here are the best practices on what to use from your public facing website style guide, and things to consider:
Don’t overbrand it or make it into an art showcase
Remember who your users are and what they need from an intranet
Don’t deviate from corporate branding to the point of being unrecognizable
Don’t replicate the public site look
It will set unnecessary expectations and confuse others
Keep fonts and colors
Keep page header simple
Majority of real estate will be used for document management; avoid taking up space
Intranet Name
The intranet name is another important aspect of branding. In fact, there are many strategies to help you come up with a creative name for your intranet including crowdsourcing with your staff.
Organizations are often afraid that crowdsourcing will produce really bad results and the company will have to either stick with it or come up with a better name. There are strategies you can use to avoid a negative outcome.
Define Intranet Purpose
It all starts with why you’re rolling out the intranet. Your staff (even if it’s just a handful of decision makers) needs to agree on that. It can’t just serve or be understood by one or two people.
Is your intranet there to:
Help people connect
To help find information
Document management
Employee engagement
All of the above?
Define key goals behind the intranet and come up with the name that suites that goal.
For example, the name “watercooler” sounds like it’s geared towards employee news, events and other employee related topics and not much of a place for corporate information or document management. If that’s your goal for the intranet - then it’s great; if not, you might want to reconsider.
Some Bad Examples
Avoid naming your intranet with generic terms such as:
“SharePoint”
“Intranet”
“Portal”
“[company name] Portal”
Abbreviations
Lengthy names
Hard to pronounce names
NOTE: Intranet URL and intranet name are not one and the same
Your intranet URL can be sharemuch.sharepoint.com due to naming restrictions but have a meaningful name for the site itself which can be used for as an intranet logo.
Logo
Intranet logo is best when it’s clear and simple, and includes your intranet name.
Things to consider:
Ensure you maintain square proportions as much as possible
Office 365, for example, uses the logo everywhere on the site and in some places, you can’t control how the system resizes it.
Avoid all white color logo
Again, office 365 out-of-the-box components use this logo everywhere. In some places you may end up with “blank” square if your logo is completely white.
Avoid intranet name + company logo together
The issue is here is that users may be confused which logo they should click on to get “back to home,“ as the logo is often link to the home page.
Another issue is that it increases the length of the logo and Office 365 may squeeze or resize the image, making it look disproportionate or cut off.
Footer
The purpose of the footer is to help the user find other important pages on the site and contact information for the intranet team.
It’s become common to have a large footer on the intranet and mimic site top navigation in it. It’s not a bad strategy but there are few things to consider:
Ensure links and information in the footer are up to date
Top navigation usually changes with the site structure automatically, the footer often gets forgotten and links become broken or obsolete.
Avoid social media icons in the footer especially if you have social media feeds on the site - this becomes duplicate information.
Keep number of sections less than 7 (see below; 4 sections already look busy)
Avoid making it flashy, it’s just a footer
Conclusion
Intranet branding goes beyond the colors of the site. It’s about the purpose and serving the content to the right audience. Make it relatable and unique enough from your company public site but not an art project on its own. Remember the resources typically available for maintaining the intranet are less than that for public site and those need to be considered.
Have a comment? Drop us a note!
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
4 Easy Steps to Effectively Prioritize Your Intranet Scope
13 Things You Should Move to Your SharePoint Intranet
Your SharePoint Intranet Adoption Success is 67% Dependent on these 5 Key Phases
SharePoint Metadata: Key Strategies for File Share Migration
Summary: Moving away from File share to SharePoint is one of the most painful exercises most organizations describe. With the structured approach, you can simplify this process to just a few workshops and end up with a rock-solid, and easy-to-find structure. Avoid using existing folder names as your new SharePoint structure and simplify existing containers first before defining metadata.
Although we’re builders of intranet-in-a-box, we often consult on the SharePoint migration projects (see our SharePoint migration plan). One of the most common challenges in any organization using file share, is migrating this old structure to SharePoint. Even with a wealth of tools available in SharePoint around content findability, such as metadata and tags, you still need input from your teams.
So, how do we go about it in just a few simple workshops?
Pre-Work
First, you’ll need to bring the right people to the table.
Here are few guiding principles:
Understand which teams own content in your existing file share
The ideal group size is 4-6 stakeholders
Ensure people in the room are content owners, and members who can assign tasks and allocate resources for their team. This doesn’t have to be the same person, hence we recommend 4-6 people per team.
Ensure everyone in the room is likely to contribute to their area and not just listen in.
Content Audit
You have picked the right people, now onto the content audit.
First, why do we need a content audit? Don’t we already know what content is in our file share?
Our experience shows the following:
Not everyone on the team knows everything about their existing file share structure
Much of the structure is obsolete, ad-hoc, with lots of catch-all folders
Every workshop we ran, had people discover something new about the content based on their peer’s input
Running the workshop (in person)
Request for participants to individually write down types of content their own and work with.
Give examples, such as project status report, project plan, risks and issues etc. This will help ideas flowing
Ensure participants work individually.
Request each participant to share their individual types of content and let others ask questions
Keep other participants’ interaction only for clarifications, not brainstorming, countering, or questioning workflow or business flow. There will be a separate activity to cover that :)
Remote participation
More often than not we work with hybrid teams where some participants are at the office and others are remote. There are facilitation techniques we use to accommodate this, which is a whole different topic, and with the right mix of technology and facilitation participants as productive as in on-site meetings. The key to the remote session is preparation and make sure everyone can contribute without feeling left out.
The Result
As a result, you will end up with a sample structure like below. And by the way, with all the pre-work to get to this point will only take about 45 min with an experienced facilitator.
Defining New Content Structure
Now that we have all the content on the table and everyone has the context of what everything is, it’s time to shape this into a tree.
The task is to: group relevant content into logical groups or clusters and assign labels to each cluster. For example: [Contract Template], [Agreement Template], and [SOW Template] can be collectively put into category called [Templates].
Towards the end of this exercise you will end up with something like this, notice how various content types cluster around themes forming what we call SharePoint Content Type:
At this point, we spent only about an hour and 1/2 and already have a good idea how the new repository will look like. Next, we finalize the structure.
Selecting Metadata and Tags
With the metadata you can group content by any number of tags, virtually creating “folders” on the fly. With the folder, you get to navigate the structure in a fixed format.
Regardless of method, you chose to structure your content, folder or metadata, using the output from the previous exercise, it’s easy to build the final structure.
Here are some guiding principles when tagging your content:
Use the auto-tagging feature in SharePoint to tag content automatically when it’s dropped into a specific library or folder (if you chose to go with folders).
Avoid creating hierarchies deeper than 3 levels. For example: [Project Alpha] -> [Deliverables] -> [Fact Sheet] is a good example of 3 level hierarchy.
Avoid manual versioning and creating folders to manage those. For example, avoid: Contract_v3_final, instead, rely on built-in versioning features to version your content.
This may sound like nothing to do with the metadata but we often see people create folders for Draft/Final documents which affect the content structure
Don’t confuse Metadata with a Document Type. This might sound obvious but people make this mistake all the time. Consider this scenario:
Should [Balance Sheet] be a content type or the [Year]?
The correct way is [Balance Sheet] as a Content-Type since and [Year] is a Metadata field.
NOTE: Content Types reflect entities around which rules are formed (archival, retention etc). Metadata, in this case [Year], is merely a descriptor/property of the entity.
As obvious as it is, many fileshare structures out there have the exact opposite in how folders are structured.
Conclusion
When we follow this collaborative approach with the client we see huge increase in adoption and decrease in support. The tempting alternative of bringing structure from fileshare will bring old problems to the new environment. We have used this approach on number of projects over the years and refined it meticulously for the best results, so if you have questions about details - drop us a note!
What are some of the challenges you found when migrating from fileshare to SharePoint? Leave your comment below.
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
Intranet Launch Check List and Activities
Can you measure the ROI of your intranet design efforts?
SharePoint Intranet Essentials and Must-haves for a Modern Intranet
7 Steps to Effectively Introduce an Employee Intranet & Digital Workplace
Remote Work Essentials: What Organizations are Missing Today
Last week we had a chance to attend Remote Work Summit to really understand the disruptive forces that remote workers are bringing to industries. Many employers are unaware of significant shift in how their teams are evolving and what it takes to keep their productivity high.
After listening to dozens of executives and managers successfully running remote teams, few patterns started to emerge which boil down to:
Managing Communication
Managing Knowledge
In this post you'll find the insight I got from managers and executives of successful remote-first companies.
Companies operate in remote-like mode without realizing it
Many large organizations these days are distributed geographically, does that mean they are remote enabled organizations? What about companies which have offices in the same city but employees of one office never meet someone from another office, have a separate lunchroom, separate boardrooms. In relation to each other these teams operate in a remote mode.
How about companies with employees on different floors rarely visiting one another. I've seen entire office events organized for members of a particular floor purely based on the job role of people on that floor. Entire teams operate in semi-remote or mixed-mode without even realizing it.
The issue with operating in remote-mode without actually realizing it is that there is lack of processes and tools which positively enable such teams to function. This results in frustrations, loss of productivity, and ultimately turnover.
So what's required to successfully make this mixed-remote environment happen?
Managing communication is all about expectations
The biggest fear of any company looking at introducing remote is that team members will not be able to get a hold of each other in time, miss deadlines and start blaming technology as an excuse.
Another fear, this time from employees, is that they will be getting messages and requests from their managers and colleagues all times of the day resulting in work creeping into their personal lives.
All this will happen without proper expectations in place.
Successful remote-first companies such as Doist, Trello, GitHub and others, set communication expectations and build culture to solidify these expectations.
It's also about the tools that let you manage your communication and not bombard you with everything as high priority request. Email is an example of such (bad) communication tool where every request that comes in has to be reviewed and prioritized by you before you determine if it's important or not.
Tools such as:
Slack
Microsoft Teams
Twist
... help solve fundamental problem of everything-is-important but it's up to you to set up the culture to get on board with that.
"[Tools] don't solve the problem, you do" - is my interpretation of city's recycling slogan from below.
But it's far more than tools and expectations, it's also about planning
Managing communications is about planning
Planning is an important part of successful communication since much of communication these days is non linear. If someone is cramming for Monday morning presentation and needs your input at 9PM on Sunday knowing you're off at this time, that's poor planning on their part. It will result in stress for both of you.
Better approach is to set and manage your deadlines and communicate them with the dependent party. This way both of you know what to expect when well ahead of time.
Tools like:
Trello
Microsoft Planner
Aha
Todoist
... are all great starting points for planning your communication and work.
Managing Knowledge is the key
Managing knowledge is the key theme in Remote Work since most of the time you can't tap someone on their shoulder and ask question.
According to Nielsen Norman research on productivity, average organization of about 10,000 people looses $8 - $13.5 million each year from employee time lost while searching for information.
When users can't find: a template, a chart, a PowerPoint deck to reuse they end up re-creating the work which can take hours or days.
This isn't a new problem, in fact it's a great practice to manage your organizational knowledge whether you have remote employees or not. With remote workforce in particular, the importance of knowledge management becomes more relevant yet.
The issue of knowledge management is my favorite problem to solve because we're in the intranet business. Just as in my previous points, there are a lot of arguments about what tool to use and which one is best. The reality is that, again, knowledge management starts with the culture of your organization. You need to understand what kind of knowledge you're storing and what is the best tool to use for that.
In our organization we use videos a lot to manage interaction requirements of the software. Among other methods we tried, videos are the best method for our culture and how our team works. We found a balance in this method and no, not every requirement is a video.
For some other organization, written requirements are best. Other organization will use requirements database or a Planner or Trello.
The key is to determine the type of information you're storing and then select a tool. If you try and retrofit tools to host your information you will end up with a lot of customization or people will just not use the tool due to it's complexity.
These aren't the only challenges in building remote workforce but these are certainly fundamentals on which things are built.
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
SharePoint Conference 2018 (SPC18) - What You Need to Know
Last week one of the most important events in SharePoint community took place - the revived and long awaited SharePoint Conference in Las Vegas.
As with any major event, there is a lot of buzz from Microsoft and community. In this post, I'll focus on key items which help understand where the product is going in next 2 years. I'll back this up with Microsoft public sources and some analysis.
Key Themes
Product is evolving - Faster than you think
When Jeff Teper gave a demo of new SharePoint spaces he mentioned something that stuck with me: it took ~18 months from writing the idea on a paper to having it demo on the stage. Now think about it, that's incredibly fast to integrate SharePoint, and VR equipment, and create authoring experience all ready to be demo'ed in such a quick timeline. What this means is that important features you see these days requested on user voice will make their way into the product in a very short time. This creates much more attractive environment for Office 365 and many customers are seeing these advantages. It also creates fast paced environment for 3rd party ISV's like Origami to innovate but not over-engineer.
Modern UI is getting more modern
Microsoft continues to invest in modern UI, picture is worth a thousand words so take a look at some of these highlights (open in new window for larger picture):
Planner Integration into modern lists
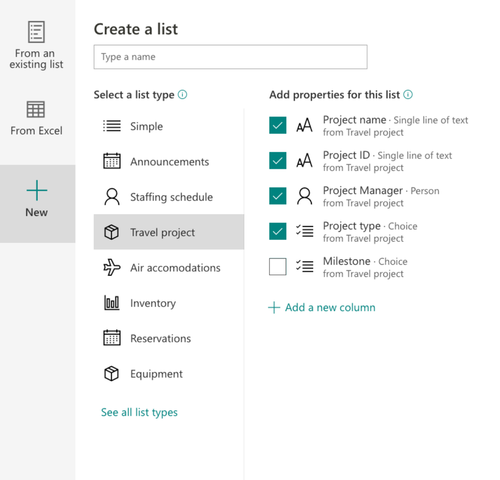
New list creation experience
More here on how to Enrich your SharePoint Content with Intelligence and Automation in a post by Chris McNulty
SharePoint 2019 On-Prem is still relevant, but customers are transitioning
During the keynote, Jeff mentioned that Microsoft is still committed to on-prem and some of the major features such as modern sites are coming to SharePoint 2019. After my sessions I spoke with a customer to whom SharePoint on-prem is the only option due to regulatory requirements. However, many more customers are now looking to transition and it's becoming lesser of an obstacle for them. Microsoft's new strategy to win users over with better and new features in Office 365 is paying off and customers are considering this less pushy environment also.
PowerBi - everywhere, effortless
PowerBI has always been interesting but unless you've set it up before it was a pain to set up to even give a demo to a customer. Few new features are coming which include PowerBI integrated and woven directly into the UI fabric.
My favorite : Lists will soon have intelligent graphs with data discovered from your list, how cool is that, no code required it's just there.
This is great for ISV's and developers since you get this new feature without having to code anything as long as your data is stored in the list, your customer will get this feature automatically.
Teams
Microsoft continues to heavily invest in Teams. It's interesting, that, from my experience, only large organizations are truly jumping on using Teams but it's still major area of focus. Few key features are coming to Teams that look interesting:
Ability to Add Planner (Schedule and Chart Views) into Teams
Coming soon ability to add custom WebParts into Teams as tabs
Full Document library feature integration
Extensibility, Workflows and Integration
As ISV, we constantly look at integration and extensibility features that platform like Office365 has. These are freebies that we don't have to spend time on. Few major announcements that make SharePoint Online more attractive in terms of extensibility include (more highlights here):
Extending search with custom sources
Run custom scripts when site is created or associated to a hub site (Powered by Flow)
Coming up: row formatter to extend how your lists look like (more here)
SharePoint FX has new capabilities to extend modern pages, lists and even sites
Should I come to SPC next year?
As a speaker you might say, I'm biased. As an advisor, my recommendation is the following.
If you're a Microsoft shop - keep a close touch and attend SPC. It's not about whether the technical or upcoming release information is available online. It's about being able to ask speakers, vendors, insiders questions that can influence your strategy. Much of the content you see posted (after the session) online get filtered. By attending live event you get bits you wouldn't know otherwise.
So, yes, do come to SPC19 in Vegas next year!
Hope this helps in your upcoming intranet design strategies. Post your comments below, would love to hear!
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.
SharePoint Online Hub Sites - What You Need to Know
[How-To]: Auto generate documents from data stored in SharePoint list and send them for signatures with DocuSign
If you're like most of us, you probably deal with a lot of document signatures. SharePoint is a great place to store those. What you don't want is to become a hub of all this communication between participants who participate in signing.
In this video, we literally take just few minutes to see how you can automate generation of e-signature enabled document based on the data stored in SharePoint list. You can then circulate the document between required parties without being involved in the logistics of the process.
The second part is being able to pick up the signed document and put it back as a list attachment, let me know if you're interested in seeing that and I'll be sure to post the solution.
Leave your comments on what are some of the things you're curious about so we can feature the most popular topics
Yaroslav Pentsarskyy is the Director of Product at Origami. He's also 8 time Microsoft MVP, speaker at many local and worldwide tech events, and a published author of several SharePoint related books.






































![How to [convince your boss] to send you to SPC18 this year?](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5c8037c77a1fbd35eda4775c/1554403844547-XP7FDBWNU2Q6YBAFG0V4/photo-1504384764586-bb4cdc1707b0.jpg)

![[How-To]: Auto generate documents from data stored in SharePoint list and send them for signatures with DocuSign](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5c8037c77a1fbd35eda4775c/1554403591116-R5Y42ZOY8WFRIBIP43J7/photo-1542744095-0d53267d353e.jpg)


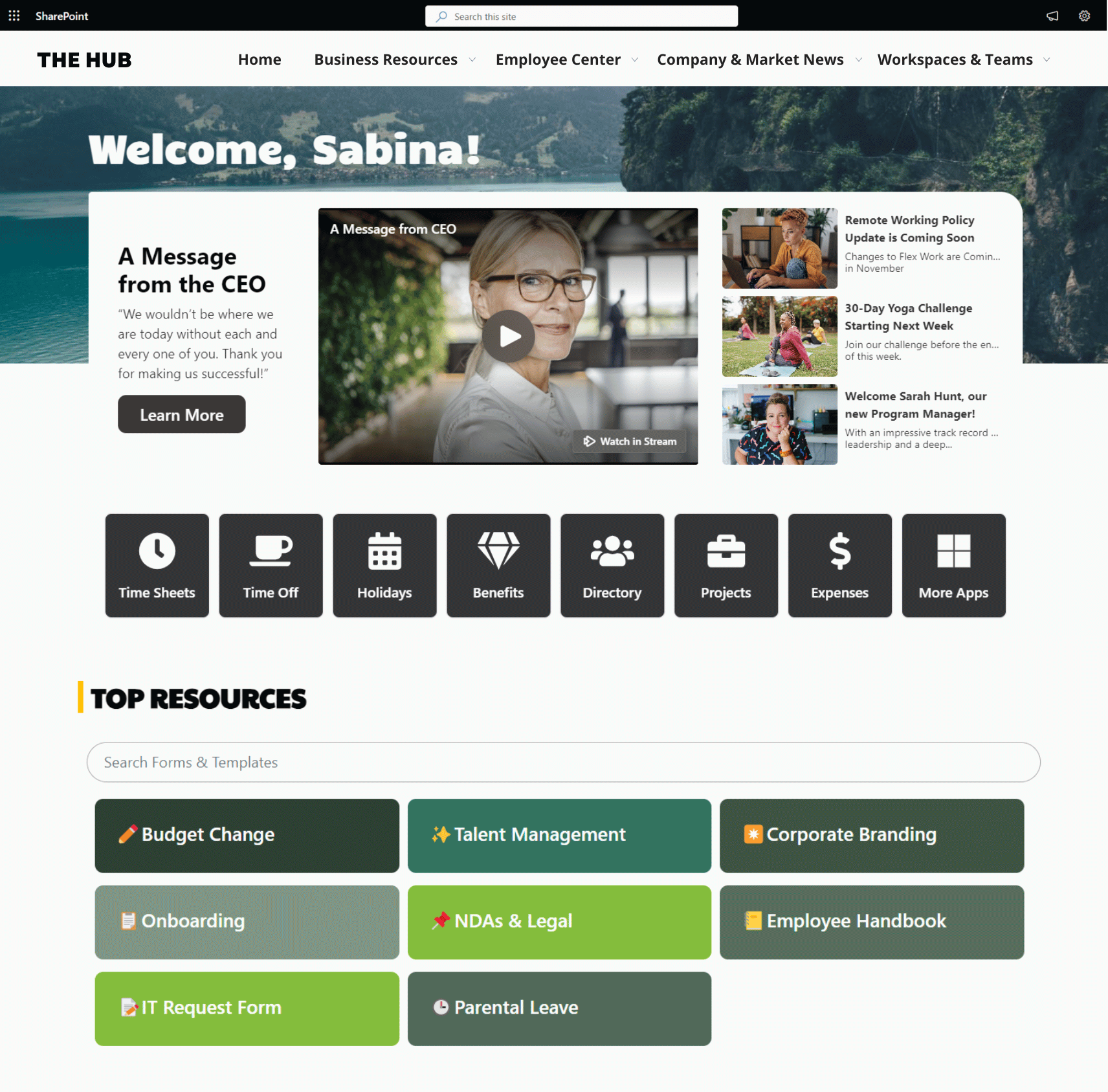
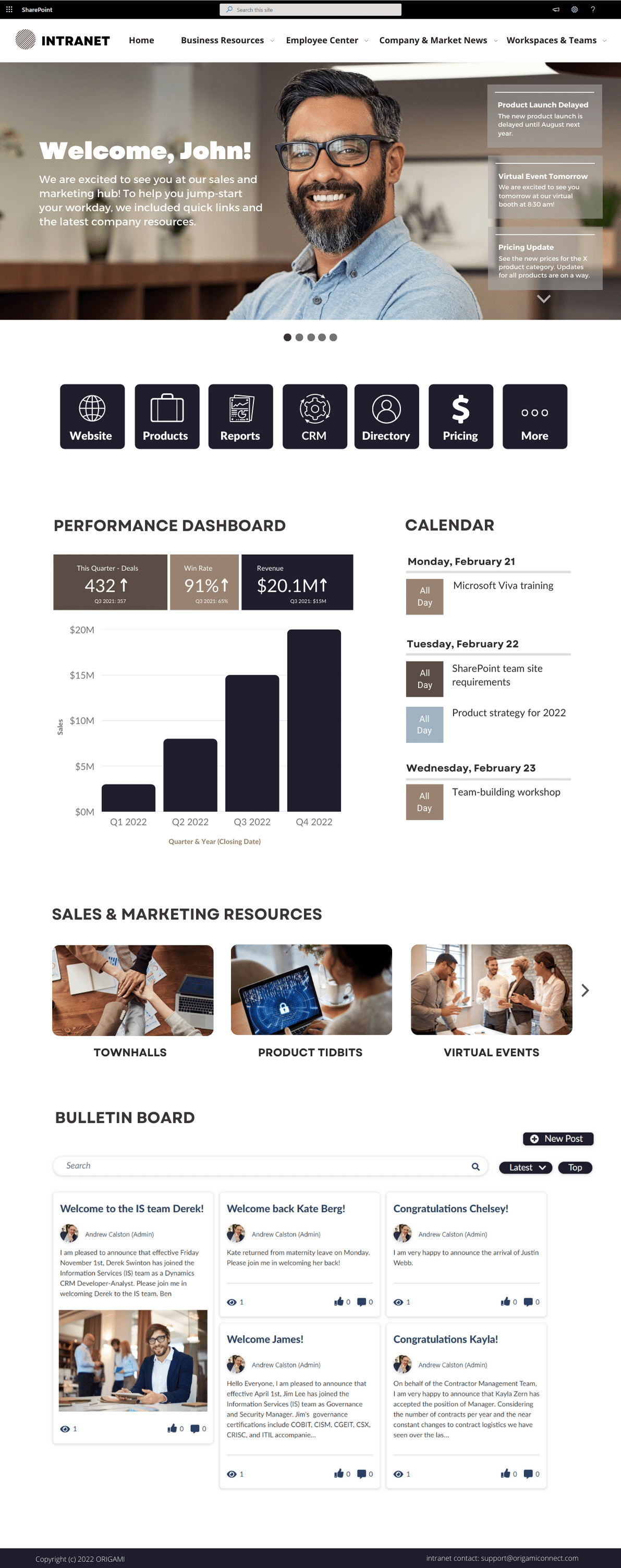
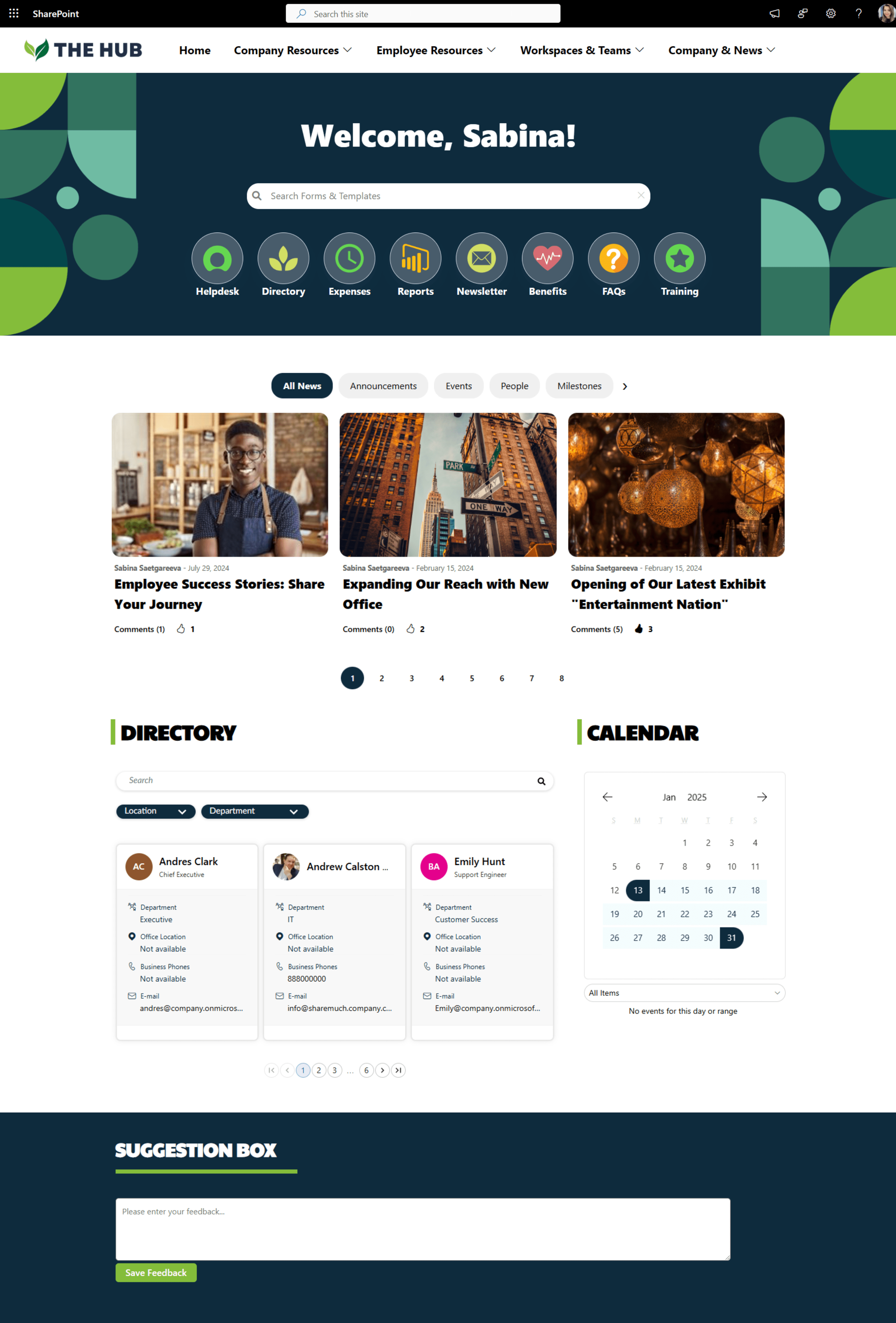
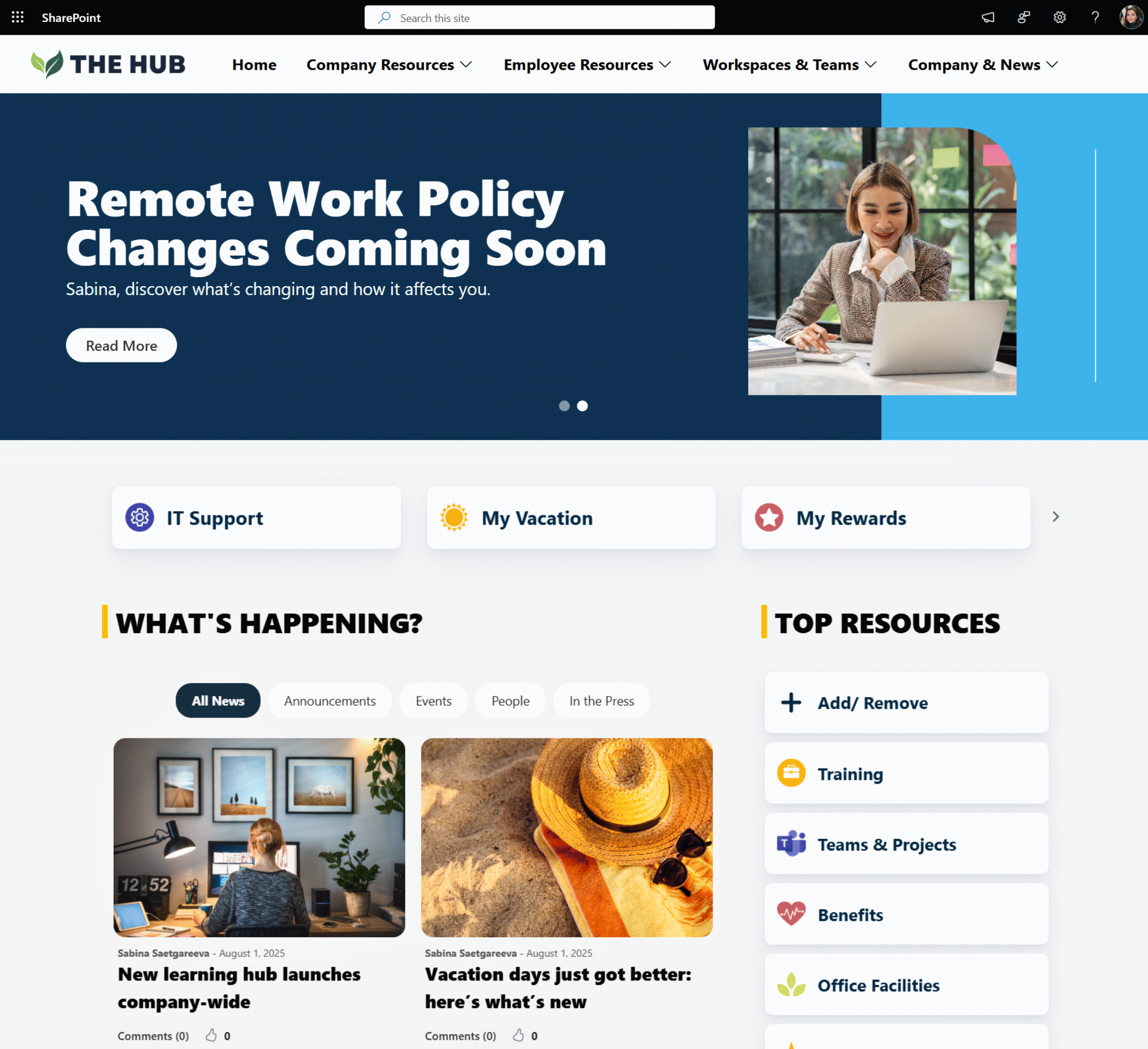
Get inspired with six company intranet examples built on data collected from hundreds of intranet sites. See intranet best practices and design ideas to help you build an intranet employees will love.